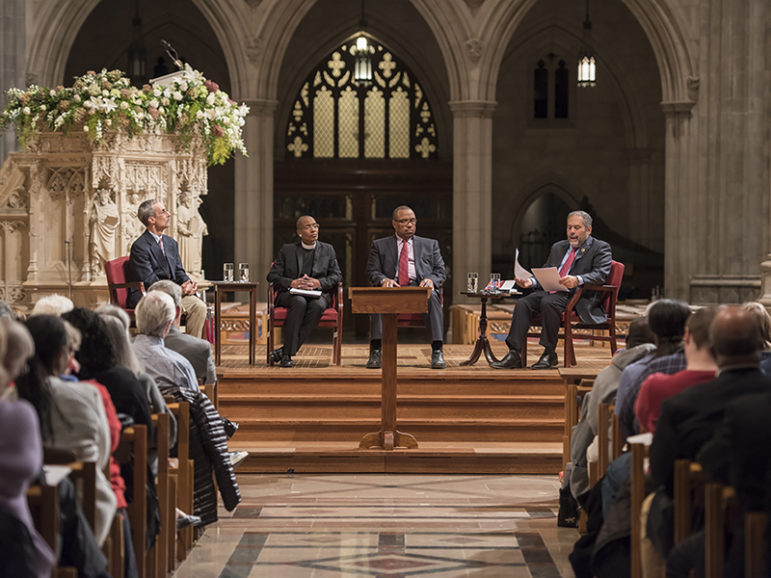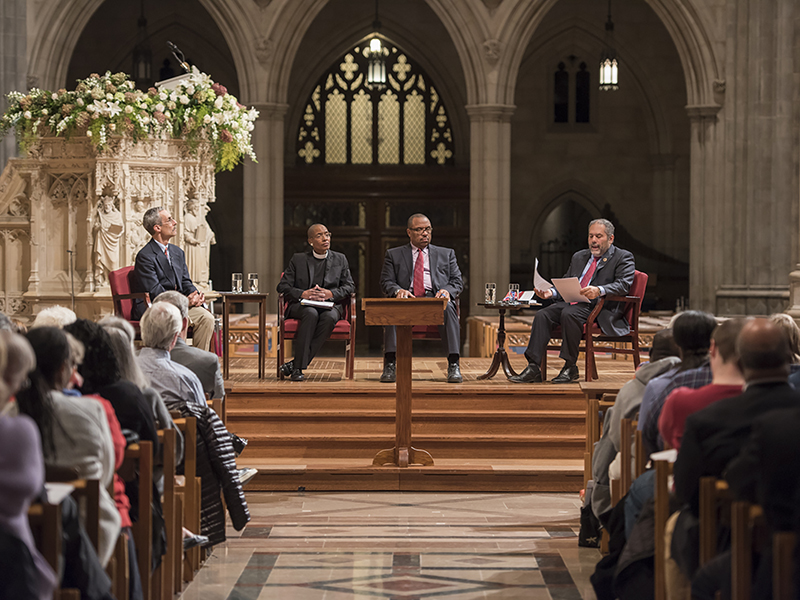
Washington National Cathedral held a discussion on its windows honoring Confederate generals on Oct. 26, 2016. Speakers, left to right, are Civil War scholar John Coski, the Rev. Kelly Brown Douglas of the cathedral, Rex Ellis of the National Museum of African American History and Culture and moderator Ray Suarez. Photo courtesy of Danielle Thomas/Washington National Cathedral
WASHINGTON (RNS) After quietly removing panes bearing the Confederate flag from its stained-glass windows, leaders of the Washington National Cathedral are now wondering what to do about remaining images of Confederate generals Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson.
“How can you justify having those windows in a house of God?” challenged Riley Temple, a former board member of the Washington National Cathedral’s foundation.
Temple was one of several audience members who spoke on Wednesday (Oct. 26) during a series of discussions the cathedral is holding on racial justice. Also present was a scholar of Civil War history and an expert from the National Museum of African American History and Culture.
The stained-glass window debate comes at a time of soul-searching in America over the legacy of slavery and renewed calls to purge public places of the Confederate flag that is for many a symbol of oppression.

Andrew Goldkuhle of Goldkuhle Studios in Hanover, Va., inspects and replaces stained-glass images of the Confederate battle flag at Washington National Cathedral. Photo courtesy of Danielle Thomas / Washington National Cathedral
The windows honoring the Confederate generals were added in 1953 with the support of the United Daughters of the Confederacy, a group that sought to honor the memory of veterans who fought for the South.
Under the Robert E. Lee window there is language etched in stone that calls him “a Christian soldier without fear and without reproach.” And under Jackson, it says he “walked humbly before his Creator whose word was his guide.”
Cathy Ball, who attends another Episcopal church in Washington, said the windows should stay.
“Our history in the United States, in America, is a history of oppression through the very beginning, the oppression of native peoples, the oppression of enslaved peoples, the oppression of immigrants,” she said.
“If we erase every trace of that terrible history, what would we have left?”
RELATED: Confederate flag images quietly removed from National Cathedral
The Rev. Kelly Brown Douglas, canon theologian at the cathedral, said she hopes the leaders will avoid the “easy route” of a take-them-down or leave-them-up decision.
“I really want to do the hard work of becoming a different kind of community, and pointing a way to how we can become that,” said Douglas, also a religion professor at Goucher College.
Nadine Wedderburn, an associate professor at Empire State College in Schenectady, N.Y., who has studied forgiveness and race relations, said discussions like the cathedral’s can be beneficial.
“People can get to air their view, share their different side of the story, as it were, and begin to get at the heart of what separates and divides us,” she said. “That is one step further towards the progress of healing and reconciliation.”