Left to right, Deepak Gerung, lead pastor of Emmanuel International Church; Kevin Zaun, lead pastor of Heartland Community Church; Paul Agamiri, lead pastor of All Nations Assembly of God; and Shawn Stoll, assistant pastor of All Nations Assembly of God, stand together at Heartland Community Church. Photo courtesy of Chris Dawes
(RNS) The Rev. Paul Agamiri made a vow when he was housed at a Kenyan refugee camp in the 1990s: If he ever made it to the United States, he would work with the white pastors in America.
A decade after he arrived in Fargo, N.D., the Sudanese man started All Nations Assembly of God in 2005 with fellow Sudanese and Liberian refugees. It now includes Africans from a dozen nations and three deacons — a Liberian, a Hutu and a Tutsi. Though just a few white worshippers join the 250 each Sunday for standing-room-only worship, Agamiri wants them to feel included.
“Many of the white people, they’re afraid to come, thinking that they would not be accepted,” Agamiri said. “White or black or whatever color, we are all connected together. We are God’s children, so there’s no worry.”
Agamiri’s church — with its swaying youth choir singing in Swahili — is the epitome of the Assemblies of God, which is marking its 100th anniversary this week from its home base in Springfield, Mo., and is the world’s largest Pentecostal denomination.
The centennial events include a summit on church planting — the process that gave birth to Agamiri’s church, which was sponsored by a parent church that has also spawned a Nepali/Bhutanese congregation. AG members from more than 100 countries will attend the celebration of the “fellowship” that has grown from 300 people gathered in Hot Springs, Ark., in April 1914 to 67.5 million adherents worldwide.

Since 2007, George O. Wood has worked as the general superintendent of the General Council of the Assemblies of God in the U.S.
The U.S. denomination alone is a veritable United Nations of some 3.1 million faithful — with a membership that is 41 percent nonwhite, up from 31 percent a decade ago.
General Superintendent George Wood said the denomination has grown because its members model the methods of the earliest followers of Jesus.
“They were tasked with taking the gospel to every nation,” said Wood, 72, who also heads the World Assemblies of God Fellowship. “The word ‘nation’ in the Greek language is ‘ethnos,’ or ethnic group. Our task, right from day one, has been to attempt to bring the gospel of Jesus Christ to the ethnic groups of this world and in this country.”
Wood and others acknowledge that the Assemblies’ racial history has not been unblemished. With roots in the interracial Azusa Street Revival that began in Los Angeles in 1906, the leaders of the Assemblies of God started out as a group of white men. Bishop Charles H. Mason of the Church of God in Christ, which would eventually become one of the largest black Pentecostal denominations, attended the Hot Springs gathering, but black and white leaders ended up leading segregated groups.
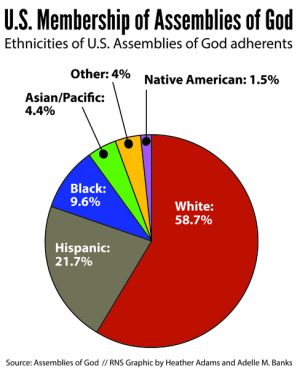
“U.S. Membership of Assemblies of God: Ethnicities of U.S. Assemblies of God adherents” graphic by Heather Adams and Adelle M. Banks, Religion News Service.
“We did have a slow start,” Wood said. “In the last number of decades, we’ve seen tremendous progress in the United States.”
He attributes the racial separation of the early years to leaders’ following the segregationist culture at the time rather than scriptural ideals.
“However, the Holy Spirit is a great corrector of behavior, and over a course of time, people more and more realized that this segregation and division among races was not ever God’s plan,” Wood said. “And so I think now, as we look over 100 years, the majority of our history has been one of inclusion rather than exclusion.”
Despite the advances in race relations, the multiethnic dynamic only goes so far.
Rice University sociologist Michael Emerson, who studies race and religion, said the Assemblies are “more diverse than most other denominations,” but that diversity doesn’t always trickle down to individual congregations.
“Forty percent of their membership is nonwhite,” he said, “but nowhere near 40 percent of their congregations are multiracial.”
During an eight-day trip in July, Scott Temple, the Assemblies’ director of ethnic relations, traveled to settings that bore out the range of what American AG churches look like. He went from a multiethnic congregation in Englewood, N.J., where 40 different nationalities worship together, to a Messianic Jewish congregation, to a biennial meeting of the denomination’s National Black Fellowship.

Scott Temple is director of the Assemblies of God Office of Ethnic Relations. Photo courtesy of Assemblies of God Office of Ethnic Relations
“My wife says I have the job because I like to eat anything,” admitted Temple, who is white and spends 120 nights a year on the road. “That’s pretty true.”
Beyond building the range of ethnic congregations, the U.S. denomination has worked to foster better relations with predominantly black groups from which it had been estranged. Last November, AG leaders invited their counterparts from the Church of God in Christ to Springfield. COGIC leaders, in turn, have invited Wood to speak at a September celebration of the 150th anniversary of the birth of Bishop Charles H. Mason, COGIC’s founder.
Since reaching agreement in February with the smaller, predominantly black United Pentecostal Council of the Assemblies of God, leaders of the two fellowships have begun to meet.
The Rev. Thomas Barclay, international presiding elder of the UPCAG, who is based in Chicago, said he attended the AG’s Illinois District meeting and received a standing ovation and apologies for the past.

“Nonwhite Assemblies of God adherents” graphic by Heather Adams and Adelle M. Banks, Religion News Service.
Grant Wacker, Duke Divinity School professor of Christian history, said the Assemblies are simultaneously increasing their outreach to Hispanics and Native Americans and retaining their strong conservative political and theological values.
“There are more and more minority worshippers who take the Assemblies of God absolutely seriously in their claim that the Holy Spirit is blind to gender and ethnic differences,” said Wacker, author of “Heaven Below,” a book on U.S. Pentecostalism.
Temple is hoping that trend continues. By 2020, he says, the AG “will be what is called a minority majority. There will be no dominant group.”
In fact, the AG’s long-term emphasis on sending missionaries overseas is now working in reverse, with immigrants like Agamiri coming to the U.S. to win souls.
“They are truly missionaries in a refugee package,” said Pastor Shawn Stoll, a white assistant pastor at Agamiri’s church. “They’re not just here as a refuge, as a place to land, but they are here in a missionary form, to reach out to the Americans and to the Africans as well.”
KRE/MG END BANKS
Click on any photo to begin this slideshow of historical photos, courtesy of the General Council of the Assemblies of God
- Members of the Assemblies of God Executive Presbytery in 1914.
- A group of Pentecostals founded the Assemblies of God denomination in 1914.
- Roberto Fierro was considered one of the 20th century’s most important bilingual and bicultural Latino Pentecostal evangelists. He preached fluently in both Spanish and English throughout the U.S. and in Spanish-speaking countries. He eventually expanded his ministry to include publications and a Spanish-language radio program.
- With the help of area churches and merchants, Cornelia Jones Robertson, “Mother Jones,” started a mission in the notorious Barbary Coast district of San Francisco that served over 100,000 men and boys over the course of 14 years. She became an ordained minister in the Northern California-Nevada District in 1923 – making her one of the first ordained African-American women in the Assemblies of God fellowship.
- David Wilkerson caught the attention of gang members as “the guy the cops don’t like.” He moved his family from a rural church in Pennsylvania to New York City where he founded Teen Challenge and Times Square Church.
- Following a difficult upbringing, twin brothers Eddie and Billie Washington accepted Christ at a revival. They, along with their spouses, ministered together for many years. In 1963, Eddie and Ruth Washington moved to Germany to serve as missionary-evangelists among European Pentecostals and American military personnel.
- A simple gesture of buying all the newspapers a boy was selling on a street corner in San Salvador stirred the heart of John Bueno and led to the opening of a Christian school in 1963. Today Latin American ChildCare represents the largest network of evangelical Christian schools in Latin America with 300 schools in 21 countries impacting the lives of nearly 100,000 children each day with food, education and medical care.
- Racial reconciliation began among white and black Pentecostals at the Pentecostal-charismatic unity meeting in Memphis, Tenn., in October 1994. The reconciliation effort became a historic three-day meeting, later called “the Memphis Miracle,” in which church leaders and scholars explored ways to heal wounds and create racial unity. The all-white Pentecostal Fellowship of North America was dissolved and replaced by the inclusive Pentecostal/ Charismatic Churches of North America.
- The first World Assemblies of God Congress convened in Seoul, South Korea, in 1989 with more than 1 million in attendance.
Subscribers, click here to download high resolution versions of select photos featured in this gallery.














